Diabetes is increasingly recognized as a lifestyle disease, primarily stemming from unhealthy eating habits and poor lifestyle choices. This rising trend has led to a significant increase in the number of people suffering from diabetes. India has the highest number of diabetes patients in the world, earning it the title of the "Diabetes Capital." It is widely believed that once someone is diagnosed with diabetes, it cannot be completely cured; it can only be managed and controlled.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is mainly classified into two types: Type 1 and Type 2.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that typically develops in childhood or early adulthood. In this type, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body cannot produce insulin, a hormone essential for converting glucose into energy. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy and regular blood sugar monitoring.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is primarily associated with lifestyle factors. It usually develops in adults, though it is increasingly being diagnosed in younger individuals due to rising obesity rates and sedentary lifestyles. In Type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. Management may involve lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin therapy.
The Rising Threat of Type 1 Diabetes
Recently, Type 1 diabetes has emerged as a serious public health issue, affecting millions globally. Its increasing prevalence raises concerns, as long-term management can lead to severe complications, including diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), coma, or even death. Current estimates suggest that approximately 70% of people in India may be living with some form of blood sugar imbalance.
Risks of Uncontrolled Blood Sugar
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial, especially for individuals with Type 1 diabetes. Uncontrolled blood sugar can lead to various negative health outcomes. Chronic high blood sugar levels can cause damage to blood vessels, nerves, eyes, and other organs. One of the severe complications of uncontrolled diabetes is diabetic ketoacidosis, a condition where the body produces high levels of ketones due to a lack of insulin. This can lead to symptoms such as rapid breathing, nausea, vomiting, and confusion.
Risk of Diabetic Coma
Experts warn that uncontrolled blood sugar levels can lead to two critical conditions: hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Both conditions pose significant risks and can lead to diabetic coma if not treated promptly. Diabetic coma occurs when blood sugar levels fluctuate drastically, causing severe disorientation or loss of consciousness.
How to Control Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is vital for individuals with diabetes. Here are some effective strategies for managing blood sugar:
Healthy Eating: Focus on a balanced diet rich in leafy green vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Minimize the intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and beverages.
Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes, especially when consuming carbohydrates, to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities like walking, cycling, swimming, or yoga can significantly improve insulin sensitivity.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes and can help manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can exacerbate complications related to diabetes. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation and discuss it with your healthcare provider.
Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7 to 8 hours of quality sleep each night, as insufficient sleep can negatively impact blood sugar levels and overall health.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can affect blood sugar control. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, deep-breathing exercises, or hobbies that you enjoy.
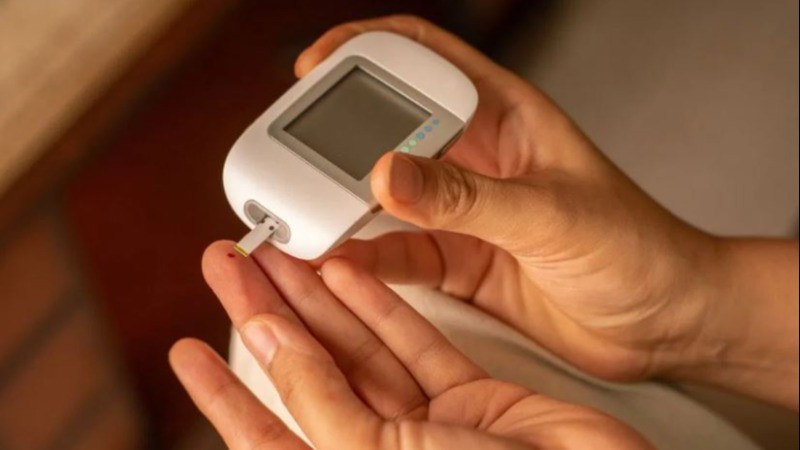
Regular Monitoring: Regularly check blood sugar levels to identify patterns and adjust dietary and lifestyle choices accordingly.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush out excess sugar through urine and maintain hydration.
How Reminders Can Help Reverse Age-Related Memory Loss
Surprising Health Benefits of Talking More: Why Seniors Should Speak Up for Better Brain
Africa CDC Raises Alarm Over Mpox Surveillance Amid Rising Cases